UNVEILING GEN Z: A DYNAMIC GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE
Welcome to an exhilarating exploration of Generation Z, the cohort born between 1997 and 2012, known for their digital prowess and transformative impact on global trends. As digital natives, Gen Zers have grown up with technology at their fingertips, shaping their unique preferences, behaviours, and values. This comprehensive global analysis dives deep into the multifaceted lives of Gen Z, examining their technology usage, environmental and social values, mental health challenges, financial outlook, and workplace expectations.
Prepare to journey through a rich tapestry of insights, drawn from diverse sources around the world, that paint a vivid picture of how this generation is redefining norms and shaping the future. From their adeptness at multitasking in the digital realm to their unwavering commitment to social justice and environmental sustainability, Gen Z stands at the forefront of change, driving innovation and demanding authenticity. Whether you are a marketer, employer, educator, or simply curious about the future, this report offers a thorough understanding of Gen Z, providing you with the knowledge to connect with and support this influential generation effectively.
Key Highlights:
Tech-Savvy Pioneers: Discover how Gen Z’s near-universal smartphone usage and preference for social commerce are revolutionizing digital interactions globally. In regions like Europe, Asia, and the Americas, their engagement with platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and WeChat is reshaping marketing strategies and consumer behaviours.
Values-Driven Advocates: Explore how Gen Z’s strong environmental and social justice values influence their choices, from the brands they support to the careers they pursue. With substantial numbers willing to switch jobs for better alignment with their values, this generation is pushing for greater corporate responsibility and transparency.
Mental Health Warriors: Understand the mental health landscape for Gen Z, including the high levels of stress they face and the progressive initiatives being implemented worldwide to address these challenges. Countries like Australia and Germany are leading the way in workplace mental health reforms.
Financial Navigators: Gain insights into Gen Z’s financial outlook, including their concerns about economic security and the impact of technology on their career trajectories. This generation is embracing alternative education paths and lifelong learning to adapt to rapidly changing job markets.
Join us as we uncover the dynamic and complex world of Generation Z, a generation poised to leave an indelible mark on society and the global economy. This analysis not only highlights the challenges and opportunities faced by Gen Z but also offers strategic insights for engaging with and supporting this vibrant and forward-thinking generation.
Social Media and Technology Use: A Global Perspective on Generation Z
Digital Natives
Pervasive Smartphone Use: Generation Z’s status as digital natives is evident across the globe, with high smartphone penetration rates reflecting their constant connectivity and reliance on mobile technology.
Europe: In Europe, 94% of teens have a smartphone, a figure that mirrors the 95% penetration rate in the US (Social Media Dashboard). Countries like the UK, Germany, and France show similar trends, highlighting the widespread adoption of mobile technology among young people.
Asia: The smartphone penetration rate among teens in Asia is equally high, with countries like South Korea and Japan leading the way. In South Korea, smartphone ownership among teens is nearly universal, driven by advanced technological infrastructure and cultural integration of digital tools into daily life (Social Media Dashboard) (Deloitte).
Social Commerce
Dominance in Social Shopping: Gen Z leads the charge in social commerce globally, leveraging social media platforms for shopping and product discovery.
United Kingdom: In the UK, 81% of Gen Z shop on social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook. This is slightly lower than the 83% in the US, reflecting a strong preference for social-first shopping experiences across both regions (Social Media Dashboard).
China: In China, platforms like WeChat and Douyin (Chinese TikTok) dominate the social shopping landscape. These platforms integrate e-commerce features seamlessly, allowing users to shop directly within the app. The local digital ecosystem supports this trend, with social commerce being a critical component of Gen Z’s shopping behavior (Mediatool) (Deloitte).
Southeast Asia: Countries in Southeast Asia, such as Indonesia and Thailand, also see high engagement in social commerce. Platforms like Shopee and Lazada, which incorporate social elements, are popular among young consumers (Mediatool).
Influencer Impact
Global Influence: Influencers play a pivotal role in shaping the purchasing decisions of Gen Z worldwide, with varying degrees of impact across regions.
Europe: In Europe, 45% of Gen Zers consider influencer recommendations critical. Influencers are viewed as relatable and trustworthy sources of information, often perceived as peers rather than celebrities (Mediatool).
United States: This figure is slightly higher in the US, where 50% of Gen Zers rely on influencer endorsements. The influencer market is highly developed, with a diverse range of micro and macro influencers shaping consumer preferences (Mediatool).
Latin America: In Latin America, 55% of Gen Z value influencer endorsements, reflecting the region’s strong social media engagement and the significant role influencers play in daily digital interactions. Countries like Brazil and Mexico show high engagement rates with influencer content (Mediatool) (Deloitte).
Search Preferences
Shift to Social Platforms for Search: There is a noticeable shift in search behaviour among Gen Z, with social media platforms increasingly being used as primary search tools.
Global Trend: Approximately 40% of Gen Zers use TikTok for search instead of traditional search engines like Google. This trend is particularly prominent in regions with high TikTok usage, such as Southeast Asia, where visual and interactive content is preferred over text-based search results (Social Media Dashboard).
Regional Variations: In the US and Europe, this shift is also evident, with Gen Z favoring platforms that offer quick, engaging, and visual content for their search queries. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok provide immediate, visually rich answers that resonate more with their consumption habits (Social Media Dashboard) (Deloitte).
Key Strategies for Engaging Gen Z Through Social Media and Technology
Embrace Mobile-first Strategies: Given the high smartphone penetration rates, brands should prioritize mobile-first strategies to reach Gen Z effectively. This includes optimizing websites and apps for mobile use and leveraging mobile-specific features like push notifications and in-app purchases.
Leverage Social Commerce: Brands should capitalize on the popularity of social commerce by integrating shopping features into their social media presence. This includes using platforms like Instagram Shopping, TikTok’s in-app shopping features, and local equivalents in other regions.
Partner with Influencers: Collaborating with influencers who resonate with Gen Z’s values and interests can significantly enhance brand visibility and credibility. Micro-influencers, in particular, can offer a more authentic connection with their audience.
Optimize for Social Search: As Gen Z increasingly uses social media platforms for search, brands should optimize their content for discoverability on these platforms. This includes using relevant hashtags, creating engaging and informative short-form videos, and maintaining an active presence on popular social media channels.
By understanding and adapting to these social media and technology trends, brands can better engage with Generation Z and build lasting relationships with this digitally savvy cohort.
Values and Beliefs: A Comprehensive Global Perspective on Generation Z
Environmental Concerns
Global Priority: Protecting the environment is a paramount concern for Generation Z across the globe. This generation is highly conscious of environmental issues and is willing to make significant lifestyle and career changes to support sustainability.
Europe: In Europe, 70% of Gen Zers are willing to switch jobs to align with their environmental values, reflecting a strong commitment to sustainability (Deloitte). This high percentage indicates a substantial willingness among young Europeans to prioritize environmental concerns over career stability.
United States: In the US, 60% of Gen Z are prepared to change jobs to ensure their work aligns with their environmental values (Deloitte). This commitment to sustainability is influenced by increasing awareness of climate change and the environmental impact of various industries.
Australia: The commitment to environmental concerns is even more pronounced in Australia, where 75% of Gen Zers prioritize environmental issues. This higher figure may be influenced by Australia's unique environmental challenges, such as frequent bushfires and biodiversity loss (Deloitte).
Asia: In countries like Japan and South Korea, there is also a strong emphasis on environmental sustainability, with a significant portion of Gen Z supporting policies and practices that mitigate environmental harm. In China, government initiatives promoting green technology and sustainability have found substantial support among young people (Deloitte).
Social Justice
Global Expectation: Gen Z expects brands to actively engage in social justice issues, reflecting their strong commitment to equity and fairness across various domains.
Canada: In Canada, 60% of Gen Zers expect brands to engage in social justice issues, a figure slightly higher than the 50% in the US. This expectation is driven by Canada’s multicultural society and its progressive stance on social issues (Mediatool).
United States: In the US, 50% of Gen Z expect brands to take a stand on social justice issues. This generation grew up during significant social movements, such as Black Lives Matter and #MeToo, which have shaped their expectations of corporate social responsibility (Mediatool).
South Africa: In South Africa, this expectation is similarly high due to the country's history of apartheid and ongoing struggles for racial equality and social justice. The country’s strong social justice movements have deeply influenced Gen Z’s values (Mediatool) (Deloitte).
Europe: Across Europe, Gen Zers are highly engaged in social justice issues, with significant support for movements advocating for racial equality, gender equality, and LGBTQ+ rights. Countries like Sweden and Germany see high levels of activism among young people (Mediatool).
Asia: In countries like India and Indonesia, there is a growing awareness and involvement in social justice issues, particularly concerning gender equality and labour rights. Young people in these regions are increasingly using social media to mobilize and advocate for change (Deloitte).
Key Strategies for Addressing Gen Z’s Values and Beliefs
Environmental Commitment: Brands and employers must demonstrate genuine commitment to environmental sustainability. This can be achieved by implementing green practices, reducing carbon footprints, and transparently communicating these efforts to Gen Z consumers and employees.
Social Responsibility: Engaging in social justice issues is crucial for brands to earn the trust and loyalty of Gen Z. This includes taking a stand on important issues, supporting social justice movements, and ensuring inclusive and equitable practices within the organization.
Transparent Communication: Transparency is key when addressing environmental and social concerns. Brands should openly share their policies, practices, and progress towards sustainability and social responsibility goals.
Authentic Engagement: Authenticity matters to Gen Z. Brands need to engage with these issues sincerely and avoid performative actions that do not lead to real change. Genuine efforts are more likely to resonate with this discerning generation.
By understanding and addressing these values and beliefs, brands and employers can build stronger, more meaningful relationships with Generation Z, fostering loyalty and driving positive change.
Mental Health and Well-being: A Global Perspective on Generation Z
High Stress Levels
Prevalence of Stress: Stress is a pervasive issue for Generation Z worldwide, influenced by various factors such as academic pressures, job insecurity, and socio-economic challenges.
United Kingdom: In the UK, 42% of Gen Zers report feeling stressed most of the time, a figure slightly higher than the 40% reported in the US (Deloitte). The main stressors include academic performance, job prospects, and the high cost of living.
United States: In the US, 40% of Gen Zers feel stressed most of the time, with significant contributors being student debt, job market competition, and social pressures (Deloitte).
India: In India, 41% of Gen Zers experience high stress levels, largely due to academic and job pressures. The intense competition in education and employment sectors, coupled with societal expectations, contributes to these high stress levels (Deloitte).
Australia: Similar trends are observed in Australia, where high academic expectations and financial pressures are primary stressors for Gen Z. Approximately 39% of Australian Gen Zers report feeling stressed most of the time (Deloitte).
Mental Health Initiatives
Challenges and Progress: Addressing mental health issues remains a significant challenge globally. However, there are positive signs of improvement in various regions.
Germany: In Germany, 32% of Gen Zers are concerned about potential discrimination if they raise mental health issues, compared to nearly 30% in the US. This fear of stigma can hinder individuals from seeking help and support (Deloitte).
United States: The situation is similar in the US, where nearly 30% of Gen Zers worry about discrimination in the workplace if they disclose mental health concerns (Deloitte).
Australia and New Zealand: Positive changes are being observed in countries like Australia and New Zealand, where workplace mental health practices are improving. Initiatives such as mental health days, flexible working conditions, and increased access to mental health resources are contributing to an overall improvement in mental health. In Australia, 55% of Gen Zers feel that their employers take mental health seriously, reflecting these positive changes (Deloitte).
Global Initiatives: There is a growing recognition of the importance of mental health globally, leading to various initiatives aimed at improving the well-being of Gen Z.
Mental Health Education: Schools and universities across Europe and North America are incorporating mental health education into their curricula, aiming to equip students with the tools to manage stress and seek help when needed (Deloitte).
Workplace Programs: Companies in regions like North America, Europe, and Asia are increasingly implementing mental health programs. These include providing access to counseling services, mental health awareness training for managers, and creating supportive workplace environments (Deloitte).
Government Policies: Governments in countries such as Canada, the UK, and Australia are introducing policies to support mental health. These policies aim to improve access to mental health care, reduce stigma, and promote mental well-being through public health campaigns (Deloitte).
Strategies for Supporting Gen Z’s Mental Health
Reducing Stigma: Efforts to reduce the stigma around mental health are crucial. This includes public awareness campaigns, education, and encouraging open conversations about mental health in schools and workplaces.
Improving Access to Care: Enhancing access to mental health care services is essential. This can be achieved through government funding, employer-provided health benefits, and the integration of mental health services into primary care.
Creating Supportive Environments: Schools and workplaces need to create supportive environments that prioritize mental well-being. This includes providing resources, flexible work/study options, and fostering a culture of acceptance and support.
Promoting Work-Life Balance: Encouraging a healthy work-life balance can help reduce stress levels. Employers can offer flexible working hours, remote work options, and ensure manageable workloads.
By addressing these mental health challenges and implementing supportive initiatives, we can significantly improve the well-being of Generation Z on a global scale.
Financial Outlook: An In-Depth Global Analysis for Generation Z
Economic Concerns
Financial Insecurity: Financial insecurity is a pervasive issue for Generation Z across the globe. Various factors, including economic instability, rising living costs, and uncertain job markets, contribute to this widespread concern.
Brazil: In Brazil, financial insecurity affects a significant portion of Gen Z, with 35% not feeling financially secure. This figure is higher than the 30% reported in the US, highlighting regional economic disparities and the broader challenges faced by young Brazilians (Deloitte).
United States: In the US, 30% of Gen Zers report financial insecurity, with many citing the high cost of living and student debt as primary concerns (Deloitte). Additionally, approximately 60% live paycheck to paycheck, similar to their counterparts in the UK (Deloitte).
United Kingdom: In the UK, 65% of Gen Zers live paycheck to paycheck, reflecting the high cost of living and economic pressures in the region. This figure aligns closely with the US, indicating similar financial challenges faced by young people in both countries (Deloitte).
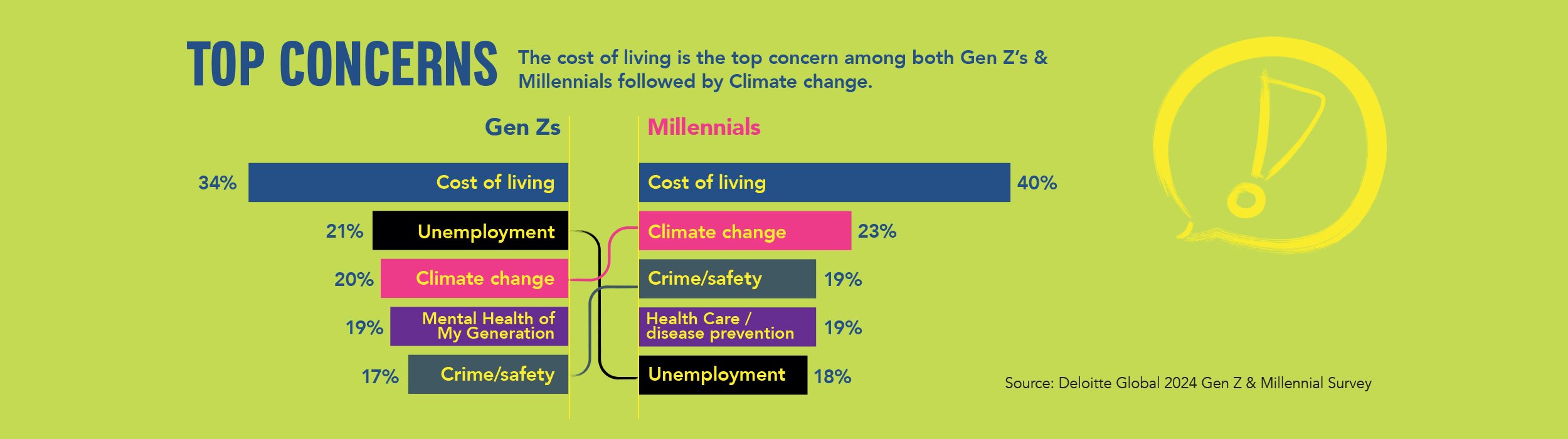
Global Concerns: Worldwide, the top financial concerns for Gen Z include the cost of living, climate change, unemployment, mental health, and crime. These issues vary in intensity by region but are universally recognized as significant stressors for the generation (Deloitte).
Education and Skills
Impact of Technology: The rapid advancement of technology, particularly AI, is reshaping the career landscape for Gen Z. This generation must adapt to new technological demands, which is influencing their education and skill development strategies.
Japan: In Japan, nearly 65% of Gen Zers anticipate that AI will impact their careers. This has led to a greater emphasis on acquiring relevant skills to remain competitive in the job market (Deloitte).
United States: In the US, 60% of Gen Z share similar concerns about AI affecting their careers, pushing them to seek alternative education paths and lifelong learning opportunities (Deloitte).
Europe: Across Europe, there is a significant shift towards alternative education models. Many Gen Zers are opting for online courses, vocational training, and continuous learning programs to stay ahead of technological advancements (Deloitte).
Asia: In regions like South Korea and India, the emphasis on STEM education is increasing, with many young people pursuing skills in coding, data analysis, and AI to enhance their career prospects. Lifelong learning is becoming a norm, with a focus on flexibility and adaptability (Deloitte).
Alternative Education Paths: The rise of online education platforms and the increasing accessibility of learning resources have provided Gen Z with more educational choices than ever before.
Online Learning: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy offer courses on various subjects, allowing Gen Z to acquire new skills outside traditional educational institutions. This flexibility is crucial for adapting to rapidly changing job requirements.
Vocational Training: Many Gen Zers are turning to vocational training programs that offer practical skills and certifications in high-demand fields such as IT, healthcare, and renewable energy. These programs are often shorter and more affordable than traditional college degrees.
Lifelong Learning: The concept of lifelong learning is gaining traction among Gen Z, with a focus on continuous personal and professional development. This approach is essential in a world where technological advancements can quickly render specific skills obsolete.
Key Strategies for Supporting Gen Z’s Financial and Educational Needs
Financial Education: Providing comprehensive financial education can help Gen Z manage their finances more effectively. Programs focusing on budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management are essential.
Accessible Education: Ensuring access to affordable and flexible education options, including online courses and vocational training, can help Gen Z acquire the skills needed for the future job market.
Support Systems: Developing robust support systems within educational institutions and workplaces can address the mental health and well-being of Gen Z. Counselling services, mentorship programs, and mental health resources are crucial.
Career Guidance: Offering career guidance and support for navigating technological changes can help Gen Z make informed decisions about their education and career paths. This includes providing information on emerging job sectors and the skills required for them.
By addressing these financial and educational challenges, we can better support Generation Z in achieving financial stability and career success in a rapidly changing world.
Consumer Behaviour: In-Depth Analysis for Generation Z
Brand Loyalty and Authenticity
High Standards for Authenticity: Generation Z is globally recognized for their high standards when it comes to brand authenticity and loyalty. Research indicates that nearly one-third of Gen Zers unfollow or block brands on social media weekly if they perceive them as inauthentic. This trend is consistent across different regions, including Europe, North America, and Asia (Social Media Dashboard) (Mediatool).
Transparency and Honesty: In regions like Europe and North America, transparency and honesty are particularly valued by Gen Z. Brands that demonstrate genuine transparency in their operations, marketing practices, and social media communications tend to gain more loyalty from this generation. For instance, brands that openly discuss their environmental impact, labour practices, and efforts towards social justice resonate more with Gen Z consumers.
Authentic Engagement: Gen Zers prefer brands that engage with them on a personal level. This includes responding to comments on social media, using user-generated content, and showcasing real customer stories. They are adept at spotting inauthentic behaviour and are quick to call out brands that appear disingenuous.
Case Study - Patagonia: An excellent example of a brand that has successfully captured Gen Z's loyalty is Patagonia. Known for its environmental activism and transparent business practices, Patagonia has built a strong, authentic relationship with young consumers globally. Their commitment to sustainability and social responsibility aligns with the core values of Gen Z, fostering deep brand loyalty.
Multi-tasking
Global Multi-taskers: Gen Z is known for their ability to multitask, with 92% engaging in multiple activities while browsing the internet. This behaviour is observed globally, indicating a widespread adaptation to consuming digital content in a highly interactive and dynamic manner (Social Media Dashboard).
Engagement with Multiple Platforms: While browsing the internet, Gen Zers often engage in activities such as eating, listening to music, talking on the phone, and interacting on social media simultaneously. This multifaceted approach to media consumption means that their attention is divided, and content must be compelling and concise to capture their interest.
Short-form Content Preference: Due to their multitasking nature, Gen Z prefers short-form content that is easily digestible. Platforms like TikTok, Instagram Stories, and Snapchat cater to this preference by providing quick, engaging content snippets. This trend underscores the importance of brevity and immediacy in digital marketing strategies aimed at Gen Z.
Visual and Interactive Content: Visual content, including videos, infographics, and memes, is particularly effective in capturing the attention of multitasking Gen Zers. Interactive content, such as polls, quizzes, and augmented reality experiences, also engages them more effectively than static posts.
Case Study - TikTok: TikTok’s success can be attributed to its alignment with Gen Z’s multitasking habits. The platform’s short, engaging videos are perfect for quick consumption, and its interactive features encourage user participation. Brands that leverage TikTok’s format can effectively reach and engage Gen Z audiences.
Key Strategies for Engaging Gen Z Consumers
Authentic Storytelling: Brands should focus on telling authentic stories that resonate with Gen Z’s values. This involves being transparent about business practices, sharing real customer experiences, and addressing social and environmental issues sincerely.
Concise and Visual Content: Given Gen Z’s preference for short-form, visual content, brands should prioritize creating concise, visually appealing content. Videos, infographics, and interactive media can effectively capture and retain their attention.
Interactive Engagement: Interactive content, such as live streams, polls, and augmented reality experiences, can engage Gen Z consumers more deeply. Encouraging user participation and creating opportunities for direct interaction with the brand can foster loyalty and engagement.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Brands that demonstrate a genuine commitment to sustainability and social responsibility are more likely to gain the loyalty of Gen Z. Transparent communication about these efforts is crucial in building trust and authenticity.
By understanding and addressing these key aspects of Gen Z’s consumer behaviour, brands can build stronger, more authentic relationships with this influential generation.
Workplace Expectations: A Global Analysis for Generation Z
Purpose-driven Work
Global Emphasis on Meaningful Employment: Generation Z places a high value on finding purpose in their work, seeking employers who are committed to community engagement and broader social impact.
Europe: In Europe, 80% of Gen Zers consider an organization’s community engagement important when choosing an employer. This reflects a strong desire for workplaces that contribute positively to society and demonstrate social responsibility (Deloitte).
United States: Similarly, in the US, 75% of Gen Z value community engagement in their employment choices. This trend is driven by a growing awareness of social and environmental issues and a desire to work for organizations that align with their personal values (Deloitte).
Australia: In Australia, the emphasis on purpose-driven work is also significant, with 78% of Gen Z considering an organization’s social impact when making career decisions. Australian Gen Zers are particularly concerned with environmental sustainability and social justice (Deloitte).
Asia: In countries like Japan and South Korea, there is a notable trend towards purpose-driven employment. Young people in these regions seek employers who are committed to sustainability and corporate social responsibility, reflecting broader societal values (Deloitte).
Implications for Employers:
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): To attract and retain Gen Z talent, companies must prioritize CSR initiatives and clearly communicate their impact on society. This includes engaging in sustainable practices, supporting community projects, and being transparent about these efforts.
Purpose Integration: Employers should integrate purpose into their organizational culture, ensuring that employees feel their work contributes to meaningful goals. This can enhance job satisfaction and loyalty among Gen Z employees.
Mental Health Stigma
Addressing Mental Health Concerns: Reducing the stigma around mental health in the workplace is a critical issue for Gen Z, who are more open about their mental health needs but still face significant barriers.
Key Strategies for Engaging Generation Z: A Comprehensive Approach
1. Authenticity in Marketing
Genuine Engagement: For Generation Z, authenticity is paramount. This generation values honesty, transparency, and real connections with brands. Traditional celebrity endorsements often fall flat with this audience, who prefer collaborations with influencers that they perceive as genuine and relatable.
Influencer Collaborations: Engaging with micro-influencers and nano-influencers who have smaller but highly engaged followings can be more effective. These influencers often share values and lifestyles similar to their audience, making their endorsements feel more personal and trustworthy. For example, brands like Mejuri and Glossier have successfully used micro-influencers to build authentic connections with their Gen Z audience (Mediatool) (Social Media Dashboard).
User-Generated Content: Encouraging and showcasing user-generated content (UGC) can enhance authenticity. UGC allows customers to share their real experiences with a brand, providing genuine testimonials that resonate more with Gen Z. Brands like Starbucks and Nike frequently use UGC to engage with their audience on social media (Social Media Dashboard).
Transparent Communication: Openly discussing business practices, behind-the-scenes operations, and corporate values helps build trust. Gen Z expects brands to be transparent about their intentions and actions, especially when it comes to social and environmental issues (Mediatool).
2. Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Commitment to Causes: Generation Z is highly conscious of social and environmental issues. They prefer brands that not only talk about sustainability and social responsibility but also demonstrate tangible commitments to these causes.
Environmental Initiatives: Companies need to integrate sustainable practices into their core operations and communicate these efforts clearly. This can include using eco-friendly materials, reducing carbon footprints, and supporting environmental projects. Brands like Patagonia and TOMS are praised for their strong environmental commitments and transparent communication about their efforts (Deloitte).
Social Responsibility: Supporting social causes such as racial equality, LGBTQ+ rights, and fair labour practices is crucial for attracting Gen Z. Brands that actively participate in and support social justice movements are more likely to gain loyalty from this generation. For instance, Ben & Jerry's is known for its strong stance on social issues, which has helped build a loyal customer base among Gen Z (Deloitte).
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Reports: Publishing detailed CSR reports can help brands maintain transparency and accountability. These reports should highlight the company’s achievements, ongoing efforts, and future goals related to sustainability and social responsibility (Deloitte).
3. Digital Adaptation
Platform Optimization: Utilizing popular social media platforms effectively is essential for engaging with Gen Z, who are digital natives and spend a significant amount of time online.
Visual and Interactive Content: Gen Z prefers visually engaging content over text-based information. Platforms like TikTok and Instagram, which emphasize short-form video content, are ideal for capturing their attention. Brands should focus on creating visually appealing, interactive, and concise content to engage this audience. Examples include interactive Instagram Stories, TikTok challenges, and augmented reality (AR) filters (Social Media Dashboard) (Deloitte).
Search Optimization: With a substantial portion of Gen Z using social media as search engines, optimizing content for discoverability on these platforms is crucial. This includes using relevant hashtags, creating SEO-friendly captions, and leveraging trending topics to increase visibility (Social Media Dashboard) (Deloitte).
Real-Time Engagement: Platforms like Instagram and Twitter enable real-time engagement, which is vital for maintaining a connection with Gen Z. Brands should be active on these platforms, responding promptly to comments and messages, and participating in trending conversations to stay relevant and visible (Deloitte).
Summary
To effectively connect with Generation Z, brands, employers, and marketers must adopt a holistic approach that encompasses authenticity, social responsibility, mental health, and digital engagement. By doing so, they can build meaningful relationships, foster loyalty, and drive positive outcomes with this influential and forward-thinking generation. Embracing these strategies will not only enhance engagement but also ensure long-term relevance in a rapidly evolving global market.
Sources:
GWI Gen Z Report, Deloitte 2024 Gen Z and Millennial Survey, Hootsuite Gen Z Statistics, Mediatool Gen Z Trends, Insider Intelligence, Pew Research, TechCrunch, Squarespace Newsroom